Prostatitis isa purely male disease. It is one of the most common lesions of the genitourinary system and occurs in approximately 80% of men, with 4 of them occurring before the age of 40.
The disease is not an isolated process: itexposes neighboring organs to trauma and also poisons the entire body.
How does prostatitis develop?
The core of the process is inflammation of the prostate or prostate gland.
The prostate is located in the pelvis, adjacent to the base of the bladder. This is an unpaired organ that looks like a chestnut. The urethra runs through it. Behind the gland is the rectum and in front of it is the pubic bone.
The prostate is a fairly elastic organ because its base consists of muscle fibers and glandular cells. It consists of 2 lobes connected by an isthmus. It is the main cause of urination problems. With age, the isthmus thickens and enlarges, putting pressure on the urethra and disrupting the process of urine excretion.
prostateperforms such functions for the body:
| function | The essence |
|---|---|
| office | Produces a secretion that is part of the sperm. It dilutes it, adjusts the required pH and increases sperm motility. |
| engine | The gland's muscle fibers form the urinary sphincter, which helps retain urine. |
| barrier | Contains a zinc-peptide complex, lysozyme, cellular immunity factors and spermine, which prevent the development of ascending infection. |
Prostatitis occurs when an inflammatory process begins in the gland. At the same time, it enlarges and narrows the urinary canal. This leads to difficulty urinating.
In addition, the enlarged prostate "invades" the bladder and squeezes it. This disrupts the outflow of urine, it stagnates and now causes inflammation in the bladder. Long-term stagnation of urinary fluid in its "reservoir" leads to poisoning of the wholeBody with metabolic products in its composition.
Decisive factors
The main reason for the development of prostatitis isinfection. These can be Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli, Proteus. The most common is prostatitisa result of sexually transmitted diseases: syphilis or gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis.
Less common is the cause of the diseaseinfectious processes of other systems: flu, tuberculosis, tonsillitis and others. Bacteria and viruses enter the prostate via the lymphatic and blood flow as well as through sexual contact. Very often, the pathogenic flora enters the gland with infected urine via the ascending route from the urethra or via the descending route from the bladder.
Other factorsInflammations of the gland include:
- Circulatory disorders in the pelvis. This can be caused by a sedentary lifestyle, obesity and pelvic injuries. A special risk group are drivers who are constantly in a sitting position and feel vibrations and pressure on the perineal area. Decreased blood circulation in the pelvis leads to congestion and lack of oxygen in the prostate, which also provokes the development of infection.
- hypothermia,
- hormonal imbalance,
- problems urinating,
- irregular sexual activity - too "violent" sex life, abstinence, interruption of sexual intercourse,
- chronic constipation,
- inflammation of the rectum,
- reduced immunity, making the body vulnerable to infectious agents.
There is an opinion that the risk of developing the disease increases with regular consumption of alcohol and drugs.
Typing and symptoms of the disease
In the modern world, the classification of prostatitis into types is carried out according to the classification of the US National Institutes of Health in 1995. Itbased on clinical data and the presence of leukocytes and pathogenic flora in semen, prostatic secretion and urine:
- Acute bacterial prostatitis.
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis.
- CPPS – chronic pelvic pain syndrome or chronic nonbacterial prostatitis.
- Asymptomatic prostatitis.
Acute prostatitisis contagious in nature. There are several phases:
- catarrhalAccompanied by frequent and painful urination. The pain radiates to the sacrum and perineum,
- follicular. The intensity of the pain increases. It also occurs during bowel movements. Urination becomes difficult - urine comes out in a thin stream or drops. Hyperthermia up to 38°,
- parenchymatous.Characterized by acute urinary retention and problems with bowel movements. Severe pain in the perineum, lower back and above the pubic bone. The body temperature rises to 38-40°. Intoxication of the body develops, the symptoms of which are general weakness, nausea and increased heart rate.
During a digital exam by a urologist, an enlarged, dense prostate gland that is hot and painful to touch is palpated. Numerous leukocytes and bacteria are detected in the urine.

Chronic prostatitiscan develop as a result of an acute illness or as an independent disease. The diagnosis is made when the process lasts 3 months or longer.
Chronic prostatitis is manifested by 3 main syndromes:
- painful.Interestingly, the prostate itself does not contain pain receptors. Pain occurs when the inflammatory process affects the nerve fibers of the small pelvis, in which there are quite a few of them. It is of a different nature. It can be insignificant or sharp and strong, even annoying at night, subsiding and reoccurring. It is localized in the sacrum, scrotum, lower back and perineum.
- dysuric.The urge to urinate becomes more frequent. She becomes sluggish and there is a feeling of a heavy, incompletely emptied bladder. The process can then improve through a compensatory increase in the size of the bladder muscles, but it soon starts again. Discharge from the urethra occurs during bowel movements.
- sexual disorders– an increase or decrease in nocturnal erections, blurred orgasm, pain during ejaculation and its acceleration. Exacerbation of sexual disorders, ultimately leading to impotence. There is a concept of psychogenic dyspotence when a man convinces himself that in his condition injuries to the intimate area are inevitable. And they are actually evolving. With the development of sexual dysfunction, a man's mood also changes: he becomes irritable and depressed.
Often the chronic form of prostatitis becomes a manifestation of hidden sexually transmitted infections.
Diagnosis of CPPSis used when clinical manifestations of prostatitis are present, but no pathogens can be detected in biological fluids (urine, ejaculate and prostatic secretion). At the same time, leukocytes are determined.
The main criterion for diagnosis is pain that does not subside within 3 months.
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome is divided into two categories: inflammatory and non-inflammatory.
Inflammatory CPPSdetermined when a large number of leukocytes are found in biological fluids. Bacteria are not detected.
Non-inflammatory CPPScharacterized by the absence of leukocytes and pathogenic flora in biological fluids.
In both cases, the symptoms of prostatitis persist.
Asymptomatic formThe disease is characterized by the absence of signs of prostatic inflammation. It is discovered accidentally during the histology of prostate tissue when the patient is prescribed a prostate biopsy. A similar procedure is prescribed, for example, if the PSA value increases.
The disease manifests itself regardless of its type (except for the asymptomatic form)., especially urinary tract diseases:
- pain when urinating,
- Weak stream or drip of urine,
- Feeling that the bladder is not completely empty.
If such symptoms occur, do not hesitate to consult a urologist. This will help stop the process in its first phase.
How do you recognize the disease?
The main criteria for making the diagnosis are the clinical picture and the patient's complaints.
But to finally confirm it,It is necessary to undergo a series of tests and examinations:
- Examination by a urologist.The doctor must perform a rectal examination of the prostate. It is inserted through the rectum with a finger. It is advisable to have a bowel movement before the examination. Manipulation determines the shape and size of the gland as well as its consistency. The procedure helps to determine the presence of tumors and inflammation in the prostate. The digital examination allows you to collect prostate secretions.
- Analysis of urine.Two portions are examined: the urine collected at the beginning of urination and the urine collected at the end of urination. 1 portion indicates the condition of the urethra, 2 – the kidneys and bladder. The presence of leukocytes in the urine above normal (15 per field of view) indicates inflammation.
- After collecting urine, a prostate massage is performed, thereby obtaining its secretion.If there is too little of it and it is not released from the urethra but remains on its walls, urine is collected after the massage. It is just as informative as the prostate discharge itself. Leukocytes (there should not be more than 10 of them) as well as lecithin grains and amyloid bodies are also determined. If the first analysis of the secretion of the gland did not reveal any abnormalities, this does not mean that there is no process. Prostatic juice can be too viscous and clog the lumen of the ducts of the affected glands. Then the secretory secretion is produced by healthy gland cells. Therefore, it is necessary to pass such an analysis several times. Cultures of urine and prostate secretions are also performed to identify the causative agent of the disease and determine sensitivity to antibiotics.
- General blood analysis.
- Analysis for the presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, bladder, TRUS,This allows you to thoroughly assess the condition of the prostate.
- Uroflowmetry.It is used to assess the rate and timing of urine excretion. It is carried out using a special apparatus consisting of sensors and a container. All the patient has to do is urinate into it as usual.
- Blood PSA- Prostate specific antigen. It is an indicator of the presence of tumor formations in the prostate gland – adenoma or cancer.
- Prostate biopsy.It is carried out if cancer is suspected.
It is necessary to take a spermogram to confirm or refute infertility.
Therapy of acute and chronic prostatitis
Acute prostatitis without complications is usually treated on an outpatient basis. In case of severe poisoning or the occurrence of complications, hospitalization is indicated.
Treatment of acute prostatitisStart with antibiotics. If the condition is severely disturbed, they are administered without waiting for the results of the analysis. They use groups of antibacterial drugs that can penetrate deep into the tissues of the prostate. They act on the types of bacteria that most often cause inflammation. These antibiotics include fluoroquinolones.

After receiving the testsAntibiotic therapy can be adjusted in different ways. It all depends on the causative agent of the disease and its sensitivity to the drug. Therapy is changed even if no effect is observed after 2 days.
In the case of acute inflammation of the prostate, the administration of painkillers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is indicated. In addition to oral medications, suppositories are also used that also have a pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory effect: suppositories with propolis based on prostate extract.
In severe poisoningcarry out detoxification therapy. To do this, use a glucose solution.
Prescribed medications that improve blood flow to the prostate. They ensure the drainage of lymph from the gland, relieve swelling and promote the elimination of toxins.
In acute prostatitis, massage of the gland is prohibited, as this can lead to the development of sepsis.
Treatment for chronic prostatitis depends on the stage of the disease.
In the acute form, antibiotics are used. In the remission stage, therapy is aimed at maintaining the normal functioning of the gland:
- Drugs that normalize microcirculation of organs.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- It is important to maintain the body's immune function, which weakens under the influence of antibiotic courses. For this purpose, patients are prescribed immunostimulants.
- If sexual dysfunction occurs, antidepressants and sedatives may be prescribed.
- Prostate massage.
- Physical therapy:
- Laser,
- Ultrasonic,
- rectal electrophoresis,
- Transrectal microwave hyperthermia.
- Physical therapy.
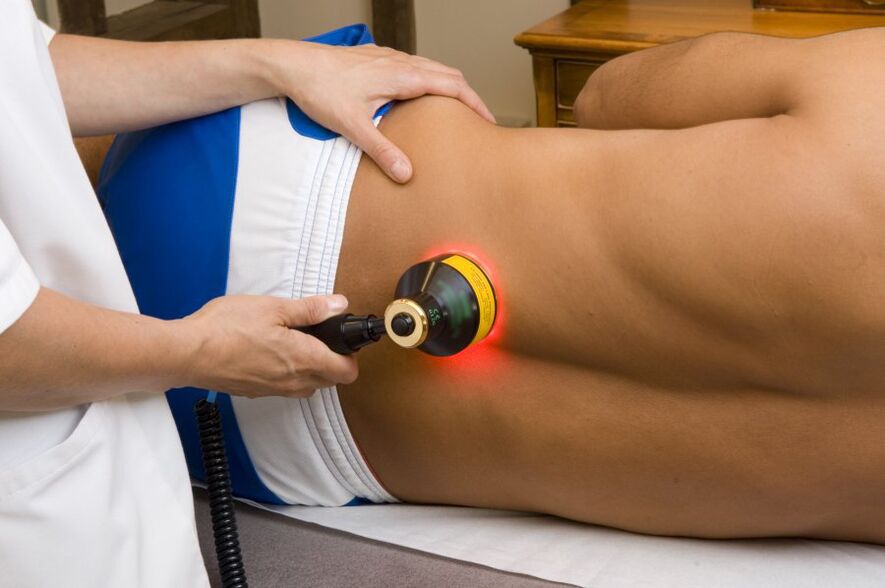
Physiotherapy for prostatitis helps to increase the tone of the pelvic floor muscles and relieve pain.
Prostate massage: purpose and technique
Finger massage of the prostate has several purposes.
It is used for diagnosis, for obtaining glandular secretions and also for treating chronic prostatitis.
The mostA common method for this procedure is transrectal. In this case, the patient is placed on his right side with his knees bent. The doctor inserts the index finger into the anus and moves it along the rectum. Then a massage is performed: gentle stroking of each lobe of the gland around it and along the ducts. At the end of the procedure, the groove between the flaps is kneaded to release secretory fluid.
It is necessary to focus on the patient's sensations: there should be no pain during the manipulation. The procedure lasts 1 minute, the entire course includes 15 sessions.
An indicator of a high-quality massage is the release of a few drops of glandular secretion.
Such manipulation is first of allincreases blood flow to the prostate. This accelerates tissue repair and improves the passage of drugs, eliminates congestion and relieves inflammation.
Massage strengthens the muscles of the gland and perineum. The procedure allows you to remove stagnant seminal fluid from the organ, thereby cleansing the prostate of bacteria and toxins. Compression of the urethra is eliminated and urination improves. A massage increases potency by increasing the circulation of semen.
In addition to the transrectal method, there is an instillation method and bougie massage.
Instillation methodbegins with the introduction of a medicinal solution through the urethra. The prostate is then clamped and massaged using the finger method. In this case, the healing solution penetrates the gland, thereby enhancing the effect of the procedure. In the end, the urethra is open, it is recommended to wait a while before urinating. The medication is reintroduced into the urethra.
Bougie massagecarried out through the urethra using bougies - special instruments for dilation and examination of tubular organs. The patient is in the right lateral position. The bougie is inserted into the urethra and held with one hand. With your second hand, stroke and press the penis from top to bottom. The duration of the procedure is 1 minute, after which the drugs are administered intraurethrally. This massage is supported by antibiotic therapy.
Finger massage of the prostate– medical manipulation carried out by a specialist according to clear indications.
One option for self-massage is possible: the muscles around the anus are rhythmically tensed and relaxed. This procedure is invisible to others and helps strengthen the gland.
Like any manipulation,Prostate massage has its contraindications:
- acute inflammation of the prostate,
- cancer or adenoma of the gland,
- Hemorrhoids,
- Stones, cystic formations in the prostate organ.
A professionally performed procedure helps to restore the structure of the prostate and its function, and stimulation of sensitive points eliminates sexual dysfunction.
Prostatitis and traditional medicine
In addition to medication, traditional methods also help in dealing with prostate inflammation.Combination of these two types of treatment, They accelerate the healing process and eliminate unpleasant sensations.
There are many home recipes that help in the fight against prostatitis. Here are some of them:
- Grind 500 grams of peeled raw pumpkin seeds through a meat grinder and mix with 200 grams of honey. Form small balls from the resulting mixture. Consume slowly twice daily before meals, chewing thoroughly and dissolving. Pumpkin seeds contain a large amount of zinc, which is essential for men's health.
- Blueberries have an anti-inflammatory effect. By consuming 200 grams of this berry per day, you will support your men's health,
- Parsley gained fame primarily as a kitchen spice. In addition, it also contains many useful substances, including those that the male body needs. Take 1 tbsp parsley juice. l. 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals. This will help reduce inflammation and improve sex life.
- Take the green peel of the chestnuts along with the thorns, chop them and pour boiling water over them. Use as tea
- Grind 300 grams of onions to a paste consistency, add 100 grams of honey and 600 ml of dry wine. Store in a dark, cool place for 1 week, stirring occasionally. Stress. Use 2 tbsp. l. 3 times a day before meals. Effective in the treatment of chronic prostatitis.
Some will help speed recoverySports exercise. They stimulate blood circulation in the pelvic area and thus also in the prostate.
- Deep squats below knee height. The optimal frequency is 100. Perform the exercise three times a week. If you cannot do such a number at once, perform squats in several approaches with breaks.
- Scissors. Sit on the floor with your hands behind you. Extend your legs in front of you and lift them off the floor. Cross them on top of each other. The movements are similar to the work of scissors.
- Lie on your back, bend your knees and bring them to your chest. Wrap your arms around her. Hold the pose for up to 20 minutes.
- Walking regularly is also a good way to relieve congestion.
You canComplement this complex with other exercisesthat activate and warm up the muscles.
Prostatitis in teenagers
It's hard to believe, but prostatitis, which was once reserved for middle-aged and older people, is now much younger and even occurs in teenagers. It negatively affects the condition of the body as a whole, as well as the reproductive ability of young people.

For this reasonIt is important to understand the reasonsthat lead to prostatitis in teenagers:
- early sexual activity and sexual illiteracy.Unprotected sexual intercourse contributes to the development of sexually transmitted infections, which can cause bacterial inflammation of the prostate.
- Hypothermia– a factor that contributes to the development of prostatitis. Temperature imbalance reduces immunity and exposes the body to infection attack.
- Fashion trends– Wearing clothes and underwear that are too tight disrupts blood circulation in the pelvis and leads to stagnation in this area.
- sedentary lifestyle– Work at the computer of modern youth replaces sports, walks and other active leisure activities.
- excessive sexual activityliterally depletes the gland. Its functions are limited, and the small amount of secretion released and the deterioration of its quality make it more susceptible to infection.
Prostatitis manifests itself in different ways in young people. Some are worried about obvious symptoms: hyperthermia, severe pain in the groin with irradiation of neighboring organs and when urinating. For others, the symptoms occur in a mild form. General weakness, decreased activity, mild fever, and urethral discharge occur.
VeryIt is important not to ignore the signs of the disease, but to start treatment in a timely manner. The neglected pathological process will leave its mark on the state of the organ and on the life of young men.
Preventive measures
It is better to prevent a disease than to treat it. Measures to prevent prostatitis are quite simple and not difficult to follow.
- First,Rethink your daily routine. If you have a sedentary job, you should definitely incorporate five-minute exercises into your daily routine. Stretch your body, move more. This is necessary so that the blood "runs" through the vessels faster. At the same time, avoid excessive physical activity, which depletes the body.
- Stop smoking. Tobacco smoke spasms blood vessels and impairs blood flow, reducing oxygen supply to the prostate. Limit consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Avoid hypothermia and nervous tension.
- It is worth consuming marinated dishes as well as spices and pickles as well as hot sauces in doses.
- Attention should be paid to regularity of sexual activity and adequacy of intercourse.
If prostatitis is left untreated, there is a risk of a number of complications: transition to a chronic form, development of infertility, spread of the process to the kidneys and bladder. More serious consequences include adenomas and prostate cancer. It is possible that purulent foci - abscesses - arise in the gland and become septic.
As you can see, the disease is quite insidious. And despite the delicate nature of the matter, you should not delay its treatment. Block the process in the early stages of its development: only in this case will you preserve your health and masculinity.